How To Create A Simple REST API in PHP? Step By Step Guide!
Previously, we learned the basics of JavaScript from our JavaScript tutorial for beginners.
Today, we will explore the creation of a simple REST API using the PHP programming language. We will delve into the implementation of CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) functionality and examine the implementation of search and pagination functionality within the context of a REST API.
This knowledge will be crucial as we utilize this API for data retrieval within our JavaScript project. Join us as we embark on this step-by-step guide to building a robust and efficient REST API.
Project Overview
What is REST API?
To define "REST API", we have to know what is "REST" is and what "API" first. I'll do my best to explain it in simple terms because REST has a lot of concepts inside of it that could mean a lot of things.
REST stands for "REpresentational State Transfer". It is a concept or architecture for managing information over the internet. REST concepts are referred to as resources. A representation of a resource must be stateless. It is usually represented by JSON. This post is worth reading: How I Explained REST to My Wife?
API stands for "Application Programming Interface." It is a set of rules that allows one software application to talk to another. Those "rules" can include the create, read, update and delete operations.
REST API enables your application to cooperate with one or several different applications using REST concepts. If you want to learn more, watch the video below.
Why do we need REST API?
REST API is needed in many applications because this is the lightest way to create, read, update or delete information between different applications over the internet or HTTP protocol. This information is presented to the user instantly, primarily if you use JavaScript to render the data on a webpage.
Where is REST API used?
REST API can be used by any application connecting to the internet. If data from an application can be created, read, updated, or deleted using another, it usually means a REST API is used.
REST API in our tutorials
A REST API is needed for our JavaScript CRUD tutorial. But don't mind it for now. We will do it one step at a time. You don't need to learn all of it as well. Just choose what you need to learn.
But one thing is for sure, this source code is good enough and works for our JavaScript tutorials.
Let's start coding!
Setup the database
Using PhpMyAdmin, create a new api_db database. Yes, api_db is the database name. After that, run the following SQL queries to create new tables with sample data.
Create categories table
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `categories` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(256) NOT NULL,
`description` text NOT NULL,
`created` datetime NOT NULL,
`modified` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 AUTO_INCREMENT=19 ;
Dump data for categories table
INSERT INTO `categories` (`id`, `name`, `description`, `created`, `modified`) VALUES
(1, 'Fashion', 'Category for anything related to fashion.', '2014-06-01 00:35:07', '2014-05-30 17:34:33'),
(2, 'Electronics', 'Gadgets, drones and more.', '2014-06-01 00:35:07', '2014-05-30 17:34:33'),
(3, 'Motors', 'Motor sports and more', '2014-06-01 00:35:07', '2014-05-30 17:34:54'),
(5, 'Movies', 'Movie products.', '0000-00-00 00:00:00', '2016-01-08 13:27:26'),
(6, 'Books', 'Kindle books, audio books and more.', '0000-00-00 00:00:00', '2016-01-08 13:27:47'),
(13, 'Sports', 'Drop into new winter gear.', '2016-01-09 02:24:24', '2016-01-09 01:24:24');
Products table
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `products` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(32) NOT NULL,
`description` text NOT NULL,
`price` decimal(10,0) NOT NULL,
`category_id` int(11) NOT NULL,
`created` datetime NOT NULL,
`modified` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1 AUTO_INCREMENT=65 ;
Dump data for products table
INSERT INTO `products` (`id`, `name`, `description`, `price`, `category_id`, `created`, `modified`) VALUES
(1, 'LG P880 4X HD', 'My first awesome phone!', '336', 3, '2014-06-01 01:12:26', '2014-05-31 17:12:26'),
(2, 'Google Nexus 4', 'The most awesome phone of 2013!', '299', 2, '2014-06-01 01:12:26', '2014-05-31 17:12:26'),
(3, 'Samsung Galaxy S4', 'How about no?', '600', 3, '2014-06-01 01:12:26', '2014-05-31 17:12:26'),
(6, 'Bench Shirt', 'The best shirt!', '29', 1, '2014-06-01 01:12:26', '2014-05-31 02:12:21'),
(7, 'Lenovo Laptop', 'My business partner.', '399', 2, '2014-06-01 01:13:45', '2014-05-31 02:13:39'),
(8, 'Samsung Galaxy Tab 10.1', 'Good tablet.', '259', 2, '2014-06-01 01:14:13', '2014-05-31 02:14:08'),
(9, 'Spalding Watch', 'My sports watch.', '199', 1, '2014-06-01 01:18:36', '2014-05-31 02:18:31'),
(10, 'Sony Smart Watch', 'The coolest smart watch!', '300', 2, '2014-06-06 17:10:01', '2014-06-05 18:09:51'),
(11, 'Huawei Y300', 'For testing purposes.', '100', 2, '2014-06-06 17:11:04', '2014-06-05 18:10:54'),
(12, 'Abercrombie Lake Arnold Shirt', 'Perfect as gift!', '60', 1, '2014-06-06 17:12:21', '2014-06-05 18:12:11'),
(13, 'Abercrombie Allen Brook Shirt', 'Cool red shirt!', '70', 1, '2014-06-06 17:12:59', '2014-06-05 18:12:49'),
(26, 'Another product', 'Awesome product!', '555', 2, '2014-11-22 19:07:34', '2014-11-21 20:07:34'),
(28, 'Wallet', 'You can absolutely use this one!', '799', 6, '2014-12-04 21:12:03', '2014-12-03 22:12:03'),
(31, 'Amanda Waller Shirt', 'New awesome shirt!', '333', 1, '2014-12-13 00:52:54', '2014-12-12 01:52:54'),
(42, 'Nike Shoes for Men', 'Nike Shoes', '12999', 3, '2015-12-12 06:47:08', '2015-12-12 05:47:08'),
(48, 'Bristol Shoes', 'Awesome shoes.', '999', 5, '2016-01-08 06:36:37', '2016-01-08 05:36:37'),
(60, 'Rolex Watch', 'Luxury watch.', '25000', 1, '2016-01-11 15:46:02', '2016-01-11 14:46:02');
Connect to database
The code below shows the database credentials and a method to get a database connection using PDO. If you're not yet familiar with PDO, please learn from our PHP OOP CRUD Tutorial first.
- Create
apifolder. Openapifolder. - Create
configfolder. Openconfigfolder. - Create a
database.phpfile. Place the following code inside it.
<?php
class Database{
// specify your own database credentials
private $host = "localhost";
private $db_name = "api_db";
private $username = "root";
private $password = "";
public $conn;
// get the database connection
public function getConnection(){
$this->conn = null;
try{
$this->conn = new PDO("mysql:host=" . $this->host . ";dbname=" . $this->db_name, $this->username, $this->password);
$this->conn->exec("set names utf8");
}catch(PDOException $exception){
echo "Connection error: " . $exception->getMessage();
}
return $this->conn;
}
}
?>
Read products
Product object
The code below shows a class named Product with several of its properties. It also shows a constructor method that will accept the database connection.
We will use this class to read data from the database.
- Open
apifolder. - Create
objectsfolder. - Open
objectsfolder. - Create
product.phpfile. - Place the following code inside it.
<?php
class Product{
// database connection and table name
private $conn;
private $table_name = "products";
// object properties
public $id;
public $name;
public $description;
public $price;
public $category_id;
public $category_name;
public $created;
// constructor with $db as database connection
public function __construct($db){
$this->conn = $db;
}
}
?>
Create file to read products
The code below shows headers about who can read this file and which type of content it will return.
In this case, our read.php the file can be read by anyone (asterisk * means all) and will return a data in JSON format.
- Open
apifolder. - Create
productfolder. - Open
productfolder. - Create
read.phpfile. - Place the following code inside it.
<?php
// required headers
header("Access-Control-Allow-Origin: *");
header("Content-Type: application/json; charset=UTF-8");
// database connection will be here
Connect to database and products table
In the code below, we included the database.php and product.php files. These are the files we created earlier.
We need to use the getConnection() method of the Database class to get a database connection. We pass this connection to the Product class.
Replace of // database connection will be here comment of read.php file with the following code.
// include database and object files
include_once '../config/database.php';
include_once '../objects/product.php';
// instantiate database and product object
$database = new Database();
$db = $database->getConnection();
// initialize object
$product = new Product($db);
// read products will be here
Read products from the database
In the code below, we used the read() method of Product class to read data from the database. Through the $num variable, we check if there are records found.
If there are records found, we loop through it using the while loop, add each record to the $products_arr array, set a 200 OK response code and show it to the user in JSON format.
Replace of // read products will be here comment of read.php file with the following code.
// query products
$stmt = $product->read();
$num = $stmt->rowCount();
// check if more than 0 record found
if($num>0){
// products array
$products_arr=array();
$products_arr["records"]=array();
// retrieve our table contents
// fetch() is faster than fetchAll()
// http://stackoverflow.com/questions/2770630/pdofetchall-vs-pdofetch-in-a-loop
while ($row = $stmt->fetch(PDO::FETCH_ASSOC)){
// extract row
// this will make $row['name'] to
// just $name only
extract($row);
$product_item=array(
"id" => $id,
"name" => $name,
"description" => html_entity_decode($description),
"price" => $price,
"category_id" => $category_id,
"category_name" => $category_name
);
array_push($products_arr["records"], $product_item);
}
// set response code - 200 OK
http_response_code(200);
// show products data in json format
echo json_encode($products_arr);
}
// no products found will be here
Add product “read()” method
We used the read() method in the previous section but it does not exist yet in the Product class. We need to add this read() method. The code below shows the query to get records from the database.
- Open
objectsfolder. - Open
product.phpfile. - Place the following code inside the
Productclass. - To make sure you added it correctly, place the code before the last closing curly brace.
// read products
function read(){
// select all query
$query = "SELECT
c.name as category_name, p.id, p.name, p.description, p.price, p.category_id, p.created
FROM
" . $this->table_name . " p
LEFT JOIN
categories c
ON p.category_id = c.id
ORDER BY
p.created DESC";
// prepare query statement
$stmt = $this->conn->prepare($query);
// execute query
$stmt->execute();
return $stmt;
}
Tell the user no products found
If the $num variable has a value of zero or negative, it means there are no records returned from the database. We need to tell the user about this.
On the code below, we set the response code to 404 - Not found and a message that says No products found.
Replace of // no products found will be here comment of read.php file with the following code.
else{
// set response code - 404 Not found
http_response_code(404);
// tell the user no products found
echo json_encode(
array("message" => "No products found.")
);
}
Output
You need to use POSTMAN to test our API. Download your version of POSTMAN here.
Launch POSTMAN. Enter the following as the request URL.
http://localhost/api/product/read.php
Click the blue "Send" button.
- Output if there are product data.

- Output if there are no product data.

Create Product
Create create.php file
- Open
productfolder. - Create a new
create.phpfile. - Open that file and put the following code inside it.
<?php
// required headers
header("Access-Control-Allow-Origin: *");
header("Content-Type: application/json; charset=UTF-8");
header("Access-Control-Allow-Methods: POST");
header("Access-Control-Max-Age: 3600");
header("Access-Control-Allow-Headers: Content-Type, Access-Control-Allow-Headers, Authorization, X-Requested-With");
// get database connection
include_once '../config/database.php';
// instantiate product object
include_once '../objects/product.php';
$database = new Database();
$db = $database->getConnection();
$product = new Product($db);
// get posted data
$data = json_decode(file_get_contents("php://input"));
// make sure data is not empty
if(
!empty($data->name) &&
!empty($data->price) &&
!empty($data->description) &&
!empty($data->category_id)
){
// set product property values
$product->name = $data->name;
$product->price = $data->price;
$product->description = $data->description;
$product->category_id = $data->category_id;
$product->created = date('Y-m-d H:i:s');
// create the product
if($product->create()){
// set response code - 201 created
http_response_code(201);
// tell the user
echo json_encode(array("message" => "Product was created."));
}
// if unable to create the product, tell the user
else{
// set response code - 503 service unavailable
http_response_code(503);
// tell the user
echo json_encode(array("message" => "Unable to create product."));
}
}
// tell the user data is incomplete
else{
// set response code - 400 bad request
http_response_code(400);
// tell the user
echo json_encode(array("message" => "Unable to create product. Data is incomplete."));
}
?>
Product create() method
- Open
objectsfolder. - Open
product.phpfile. - The previous section will not work without the following code inside the Product (objects/product.php) class.
// create product
function create(){
// query to insert record
$query = "INSERT INTO
" . $this->table_name . "
SET
name=:name, price=:price, description=:description, category_id=:category_id, created=:created";
// prepare query
$stmt = $this->conn->prepare($query);
// sanitize
$this->name=htmlspecialchars(strip_tags($this->name));
$this->price=htmlspecialchars(strip_tags($this->price));
$this->description=htmlspecialchars(strip_tags($this->description));
$this->category_id=htmlspecialchars(strip_tags($this->category_id));
$this->created=htmlspecialchars(strip_tags($this->created));
// bind values
$stmt->bindParam(":name", $this->name);
$stmt->bindParam(":price", $this->price);
$stmt->bindParam(":description", $this->description);
$stmt->bindParam(":category_id", $this->category_id);
$stmt->bindParam(":created", $this->created);
// execute query
if($stmt->execute()){
return true;
}
return false;
}
Output
To test for the successful creation of a product, open POSTMAN. Enter the following as the request URL
http://localhost/api/product/create.php
- Click the "Body" tab.
- Click "raw".
- Enter this JSON value:
{
"name" : "Amazing Pillow 2.0",
"price" : "199",
"description" : "The best pillow for amazing programmers.",
"category_id" : 2,
"created" : "2018-06-01 00:35:07"
}
- It should look like this:

- If the system is unable to create the product, it should look like this:

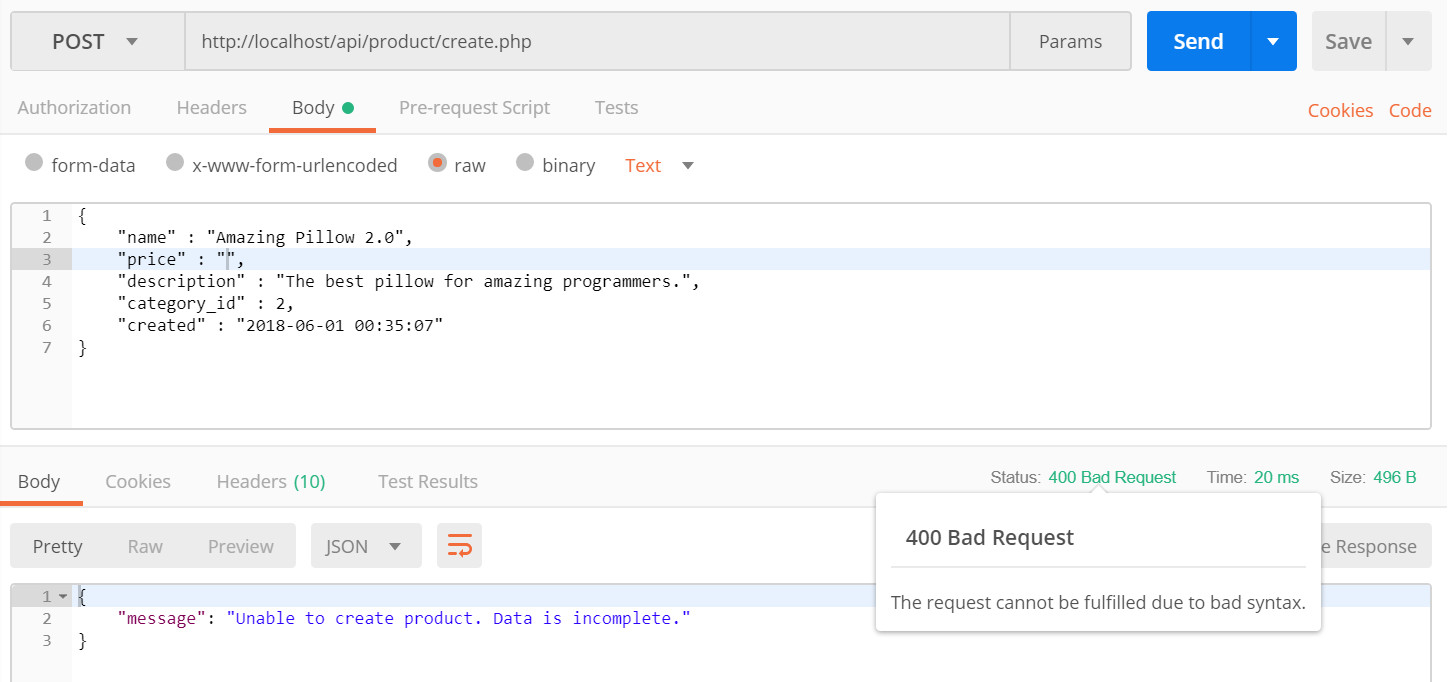
- If the sent data is incomplete, for example, it is missing the price data, the output should look like this:
Read One Product
Create read_one.php file
- Open
productfolder. - Create a w
read_one.phpfile. - Open that file and put the following code.
<?php
// required headers
header("Access-Control-Allow-Origin: *");
header("Access-Control-Allow-Headers: access");
header("Access-Control-Allow-Methods: GET");
header("Access-Control-Allow-Credentials: true");
header('Content-Type: application/json');
// include database and object files
include_once '../config/database.php';
include_once '../objects/product.php';
// get database connection
$database = new Database();
$db = $database->getConnection();
// prepare product object
$product = new Product($db);
// set ID property of record to read
$product->id = isset($_GET['id']) ? $_GET['id'] : die();
// read the details of product to be edited
$product->readOne();
if($product->name!=null){
// create array
$product_arr = array(
"id" => $product->id,
"name" => $product->name,
"description" => $product->description,
"price" => $product->price,
"category_id" => $product->category_id,
"category_name" => $product->category_name
);
// set response code - 200 OK
http_response_code(200);
// make it json format
echo json_encode($product_arr);
}
else{
// set response code - 404 Not found
http_response_code(404);
// tell the user product does not exist
echo json_encode(array("message" => "Product does not exist."));
}
?>
Product readOne() method
- Open
objectsfolder. - Open
product.phpfile. - The previous section will not work without the following code inside the
Productclass.
// used when filling up the update product form
function readOne(){
// query to read single record
$query = "SELECT
c.name as category_name, p.id, p.name, p.description, p.price, p.category_id, p.created
FROM
" . $this->table_name . " p
LEFT JOIN
categories c
ON p.category_id = c.id
WHERE
p.id = ?
LIMIT
0,1";
// prepare query statement
$stmt = $this->conn->prepare( $query );
// bind id of product to be updated
$stmt->bindParam(1, $this->id);
// execute query
$stmt->execute();
// get retrieved row
$row = $stmt->fetch(PDO::FETCH_ASSOC);
// set values to object properties
$this->name = $row['name'];
$this->price = $row['price'];
$this->description = $row['description'];
$this->category_id = $row['category_id'];
$this->category_name = $row['category_name'];
}
Output
- First, we will test for a product that exists. Open POSTMAN. Enter the following as the request URL. Click the blue "Send" button.
http://localhost/api/product/read_one.php?id=60

- Next, we will test for a product that does not exist. Enter the following as the request URL. Click the blue "Send" button.
http://localhost/api/product/read_one.php?id=999

Update product
Create “update.php” file
- Open
productfolder. - Create a new
update.phpfile. - Open that file and put the following code inside it.
<?php
// required headers
header("Access-Control-Allow-Origin: *");
header("Content-Type: application/json; charset=UTF-8");
header("Access-Control-Allow-Methods: POST");
header("Access-Control-Max-Age: 3600");
header("Access-Control-Allow-Headers: Content-Type, Access-Control-Allow-Headers, Authorization, X-Requested-With");
// include database and object files
include_once '../config/database.php';
include_once '../objects/product.php';
// get database connection
$database = new Database();
$db = $database->getConnection();
// prepare product object
$product = new Product($db);
// get id of product to be edited
$data = json_decode(file_get_contents("php://input"));
// set ID property of product to be edited
$product->id = $data->id;
// set product property values
$product->name = $data->name;
$product->price = $data->price;
$product->description = $data->description;
$product->category_id = $data->category_id;
// update the product
if($product->update()){
// set response code - 200 ok
http_response_code(200);
// tell the user
echo json_encode(array("message" => "Product was updated."));
}
// if unable to update the product, tell the user
else{
// set response code - 503 service unavailable
http_response_code(503);
// tell the user
echo json_encode(array("message" => "Unable to update product."));
}
?>
Product update() method
- Open
objectsfolder. - Open
product.phpfile. - The previous section will not work without the following code inside the Product class.
// update the product
function update(){
// update query
$query = "UPDATE
" . $this->table_name . "
SET
name = :name,
price = :price,
description = :description,
category_id = :category_id
WHERE
id = :id";
// prepare query statement
$stmt = $this->conn->prepare($query);
// sanitize
$this->name=htmlspecialchars(strip_tags($this->name));
$this->price=htmlspecialchars(strip_tags($this->price));
$this->description=htmlspecialchars(strip_tags($this->description));
$this->category_id=htmlspecialchars(strip_tags($this->category_id));
$this->id=htmlspecialchars(strip_tags($this->id));
// bind new values
$stmt->bindParam(':name', $this->name);
$stmt->bindParam(':price', $this->price);
$stmt->bindParam(':description', $this->description);
$stmt->bindParam(':category_id', $this->category_id);
$stmt->bindParam(':id', $this->id);
// execute the query
if($stmt->execute()){
return true;
}
return false;
}
Output
Open POSTMAN. Enter the following as the request URL.
http://localhost/api/product/update.php
- Click the "Body" tab.
- Click "raw".
- Enter the following JSON value.
- Make sure the ID exists in your database.
- Click the blue "Send" button.
{
"id" : "106",
"name" : "Amazing Pillow 3.0",
"price" : "255",
"description" : "The best pillow for amazing programmers.",
"category_id" : 2,
"created" : "2018-08-01 00:35:07"
}
The product ID 106, is just an example. You need to specify a product ID that exists in your database.
If you specify an ID that does not exist in the database, it might still say that the product was updated. It does not update anything on the database but the query was executed successfully without any syntax errors.
To prevent this, you need an extra validation where you check if an ID exists in the database. This feature is not yet part of our tutorial.
- If updating a product is successful, it should look like this:

- If the system fails to update the product, the output will look like this:

Delete Product
Create “delete.php” file
- Open
productfolder. - Create new
delete.phpfile. - Open that file and put the following code inside it.
<?php
// required headers
header("Access-Control-Allow-Origin: *");
header("Content-Type: application/json; charset=UTF-8");
header("Access-Control-Allow-Methods: POST");
header("Access-Control-Max-Age: 3600");
header("Access-Control-Allow-Headers: Content-Type, Access-Control-Allow-Headers, Authorization, X-Requested-With");
// include database and object file
include_once '../config/database.php';
include_once '../objects/product.php';
// get database connection
$database = new Database();
$db = $database->getConnection();
// prepare product object
$product = new Product($db);
// get product id
$data = json_decode(file_get_contents("php://input"));
// set product id to be deleted
$product->id = $data->id;
// delete the product
if($product->delete()){
// set response code - 200 ok
http_response_code(200);
// tell the user
echo json_encode(array("message" => "Product was deleted."));
}
// if unable to delete the product
else{
// set response code - 503 service unavailable
http_response_code(503);
// tell the user
echo json_encode(array("message" => "Unable to delete product."));
}
?>
Product delete() method
- Open
objectsfolder. - Open
product.phpfile. - The previous section will not work without the following code inside the
Productclass.
// delete the product
function delete(){
// delete query
$query = "DELETE FROM " . $this->table_name . " WHERE id = ?";
// prepare query
$stmt = $this->conn->prepare($query);
// sanitize
$this->id=htmlspecialchars(strip_tags($this->id));
// bind id of record to delete
$stmt->bindParam(1, $this->id);
// execute query
if($stmt->execute()){
return true;
}
return false;
}
Output
Open POSTMAN. Enter the following as the request URL.
http://localhost/api/product/delete.php
- Click the "Body" tab.
- Click "raw".
- Enter the following JSON value.
- Make sure the ID exists in your database.
- Click the blue "Send" button.
{
"id" : "106"
}
- If a product was successfully deleted, it should look like this:

- If the system fails to delete the product, the output will look like this:

Search Products
Create “search.php” file
- Open
productfolder. - Create a
search.phpfile. - Open that file and place the following code.
<?php
// required headers
header("Access-Control-Allow-Origin: *");
header("Content-Type: application/json; charset=UTF-8");
// include database and object files
include_once '../config/core.php';
include_once '../config/database.php';
include_once '../objects/product.php';
// instantiate database and product object
$database = new Database();
$db = $database->getConnection();
// initialize object
$product = new Product($db);
// get keywords
$keywords=isset($_GET["s"]) ? $_GET["s"] : "";
// query products
$stmt = $product->search($keywords);
$num = $stmt->rowCount();
// check if more than 0 record found
if($num>0){
// products array
$products_arr=array();
$products_arr["records"]=array();
// retrieve our table contents
// fetch() is faster than fetchAll()
// http://stackoverflow.com/questions/2770630/pdofetchall-vs-pdofetch-in-a-loop
while ($row = $stmt->fetch(PDO::FETCH_ASSOC)){
// extract row
// this will make $row['name'] to
// just $name only
extract($row);
$product_item=array(
"id" => $id,
"name" => $name,
"description" => html_entity_decode($description),
"price" => $price,
"category_id" => $category_id,
"category_name" => $category_name
);
array_push($products_arr["records"], $product_item);
}
// set response code - 200 OK
http_response_code(200);
// show products data
echo json_encode($products_arr);
}
else{
// set response code - 404 Not found
http_response_code(404);
// tell the user no products found
echo json_encode(
array("message" => "No products found.")
);
}
?>
Create search() method
- Open
objectsfolder. - Open
product.phpfile. - Add the following search() method.
// search products
function search($keywords){
// select all query
$query = "SELECT
c.name as category_name, p.id, p.name, p.description, p.price, p.category_id, p.created
FROM
" . $this->table_name . " p
LEFT JOIN
categories c
ON p.category_id = c.id
WHERE
p.name LIKE ? OR p.description LIKE ? OR c.name LIKE ?
ORDER BY
p.created DESC";
// prepare query statement
$stmt = $this->conn->prepare($query);
// sanitize
$keywords=htmlspecialchars(strip_tags($keywords));
$keywords = "%{$keywords}%";
// bind
$stmt->bindParam(1, $keywords);
$stmt->bindParam(2, $keywords);
$stmt->bindParam(3, $keywords);
// execute query
$stmt->execute();
return $stmt;
}
Output
Open POSTMAN. Enter the following as the request URL.
http://localhost/api/product/search.php?s=shirt
Click the blue "Send" button.
- If there was a product found, it should look like this:

- If there are no products found, the output will look like this:

Paginate Products
Create “read_paging.php” file
- Open
productfolder. - Create
read_paging.phpfile.
<?php
// required headers
header("Access-Control-Allow-Origin: *");
header("Content-Type: application/json; charset=UTF-8");
// include database and object files
include_once '../config/core.php';
include_once '../shared/utilities.php';
include_once '../config/database.php';
include_once '../objects/product.php';
// utilities
$utilities = new Utilities();
// instantiate database and product object
$database = new Database();
$db = $database->getConnection();
// initialize object
$product = new Product($db);
// query products
$stmt = $product->readPaging($from_record_num, $records_per_page);
$num = $stmt->rowCount();
// check if more than 0 record found
if($num>0){
// products array
$products_arr=array();
$products_arr["records"]=array();
$products_arr["paging"]=array();
// retrieve our table contents
// fetch() is faster than fetchAll()
// http://stackoverflow.com/questions/2770630/pdofetchall-vs-pdofetch-in-a-loop
while ($row = $stmt->fetch(PDO::FETCH_ASSOC)){
// extract row
// this will make $row['name'] to
// just $name only
extract($row);
$product_item=array(
"id" => $id,
"name" => $name,
"description" => html_entity_decode($description),
"price" => $price,
"category_id" => $category_id,
"category_name" => $category_name
);
array_push($products_arr["records"], $product_item);
}
// include paging
$total_rows=$product->count();
$page_url="{$home_url}product/read_paging.php?";
$paging=$utilities->getPaging($page, $total_rows, $records_per_page, $page_url);
$products_arr["paging"]=$paging;
// set response code - 200 OK
http_response_code(200);
// make it json format
echo json_encode($products_arr);
}
else{
// set response code - 404 Not found
http_response_code(404);
// tell the user products does not exist
echo json_encode(
array("message" => "No products found.")
);
}
?>
Create “core.php” file
This file holds our core configuration like the home URL and pagination variables.
- Open the
configfolder. - Create
core.phpfile. - Open
core.phpfile. - Place the following code.
<?php
// show error reporting
ini_set('display_errors', 1);
error_reporting(E_ALL);
// home page url
$home_url="http://localhost/api/";
// page given in URL parameter, default page is one
$page = isset($_GET['page']) ? $_GET['page'] : 1;
// set number of records per page
$records_per_page = 5;
// calculate for the query LIMIT clause
$from_record_num = ($records_per_page * $page) - $records_per_page;
?>
Create “readPaging()” method
- Open
objectsfolder. - Open
product.phpfile. - Add the following method inside the product class.
- This method will return a list of records limited to what we set in
$records_per_pageof the previous section.
// read products with pagination
public function readPaging($from_record_num, $records_per_page){
// select query
$query = "SELECT
c.name as category_name, p.id, p.name, p.description, p.price, p.category_id, p.created
FROM
" . $this->table_name . " p
LEFT JOIN
categories c
ON p.category_id = c.id
ORDER BY p.created DESC
LIMIT ?, ?";
// prepare query statement
$stmt = $this->conn->prepare( $query );
// bind variable values
$stmt->bindParam(1, $from_record_num, PDO::PARAM_INT);
$stmt->bindParam(2, $records_per_page, PDO::PARAM_INT);
// execute query
$stmt->execute();
// return values from database
return $stmt;
}
Create “count()” method
Still in the product class (product.php file), add the following method. The total rows are needed to build the pagination array. It is included in the 'paging' computation.
// used for paging products
public function count(){
$query = "SELECT COUNT(*) as total_rows FROM " . $this->table_name . "";
$stmt = $this->conn->prepare( $query );
$stmt->execute();
$row = $stmt->fetch(PDO::FETCH_ASSOC);
return $row['total_rows'];
}
Get “paging” array
- Create
sharedfolder. - Open
sharedfolder. - Create
utilities.phpfile. - Open
utilities.phpfile and place the following code.
<?php
class Utilities{
public function getPaging($page, $total_rows, $records_per_page, $page_url){
// paging array
$paging_arr=array();
// button for first page
$paging_arr["first"] = $page>1 ? "{$page_url}page=1" : "";
// count all products in the database to calculate total pages
$total_pages = ceil($total_rows / $records_per_page);
// range of links to show
$range = 2;
// display links to 'range of pages' around 'current page'
$initial_num = $page - $range;
$condition_limit_num = ($page + $range) + 1;
$paging_arr['pages']=array();
$page_count=0;
for($x=$initial_num; $x<$condition_limit_num; $x++){
// be sure '$x is greater than 0' AND 'less than or equal to the $total_pages'
if(($x > 0) && ($x <= $total_pages)){
$paging_arr['pages'][$page_count]["page"]=$x;
$paging_arr['pages'][$page_count]["url"]="{$page_url}page={$x}";
$paging_arr['pages'][$page_count]["current_page"] = $x==$page ? "yes" : "no";
$page_count++;
}
}
// button for last page
$paging_arr["last"] = $page<$total_pages ? "{$page_url}page={$total_pages}" : "";
// json format
return $paging_arr;
}
}
?>
Output
Open POSTMAN. Enter the following as the request URL.
http://localhost/api/product/read_paging.php
Click the blue "Send" button.
- If there are products found, scroll down to see the
pagingnode. It should look like this:

- If there are no products found, the output will look like this:

Read Categories
Create “category.php” file
- Open
objectsfolder. - Create new
category.phpfile. - Place the following code inside the
category.phpfile.
<?php
class Category{
// database connection and table name
private $conn;
private $table_name = "categories";
// object properties
public $id;
public $name;
public $description;
public $created;
public function __construct($db){
$this->conn = $db;
}
// used by select drop-down list
public function readAll(){
//select all data
$query = "SELECT
id, name, description
FROM
" . $this->table_name . "
ORDER BY
name";
$stmt = $this->conn->prepare( $query );
$stmt->execute();
return $stmt;
}
}
?>
Create “read.php” file
- Create new
categoryfolder. - Open that folder and create new
read.phpfile inside it. - Open
read.phpfile and place the following code.
<?php
// required header
header("Access-Control-Allow-Origin: *");
header("Content-Type: application/json; charset=UTF-8");
// include database and object files
include_once '../config/database.php';
include_once '../objects/category.php';
// instantiate database and category object
$database = new Database();
$db = $database->getConnection();
// initialize object
$category = new Category($db);
// query categorys
$stmt = $category->read();
$num = $stmt->rowCount();
// check if more than 0 record found
if($num>0){
// products array
$categories_arr=array();
$categories_arr["records"]=array();
// retrieve our table contents
// fetch() is faster than fetchAll()
// http://stackoverflow.com/questions/2770630/pdofetchall-vs-pdofetch-in-a-loop
while ($row = $stmt->fetch(PDO::FETCH_ASSOC)){
// extract row
// this will make $row['name'] to
// just $name only
extract($row);
$category_item=array(
"id" => $id,
"name" => $name,
"description" => html_entity_decode($description)
);
array_push($categories_arr["records"], $category_item);
}
// set response code - 200 OK
http_response_code(200);
// show categories data in json format
echo json_encode($categories_arr);
}
else{
// set response code - 404 Not found
http_response_code(404);
// tell the user no categories found
echo json_encode(
array("message" => "No categories found.")
);
}
?>
Add Category “read()” method
- Open
objectsfolder. - Open
category.phpfile. - The previous section's code will not work without the following code inside the
category.phpfile. - Add the following method inside the
Categoryclass.
// used by select drop-down list
public function read(){
//select all data
$query = "SELECT
id, name, description
FROM
" . $this->table_name . "
ORDER BY
name";
$stmt = $this->conn->prepare( $query );
$stmt->execute();
return $stmt;
}
Output
Open POSTMAN. Enter the following as the request URL.
http://localhost/api/category/read.php
Click the blue "Send" button.
- If there are categories found, it should look like this:

- If there are no categories found, the output will look like this:

Download Source Codes
Choose your download
| FEATURES | BASIC | PRO |
|---|---|---|
| Create product | ✔ | ✔ |
| Read products | ✔ | ✔ |
| Read one product | ✔ | ✔ |
| Update product | ✔ | ✔ |
| Delete product | ✔ | ✔ |
| Search products | ✔ | ✔ |
| Paginate products | ✔ | ✔ |
| Read categories | ✔ | ✔ |
| Delete selected product | - | ✔ |
| Export product CSV | - | ✔ |
| Read products by category | - | ✔ |
| Search products with pagination | - | ✔ |
| Create category | - | ✔ |
| Read categories | - | ✔ |
| Read one category | - | ✔ |
| Update category | - | ✔ |
| Delete category | - | ✔ |
| Search categories | - | ✔ |
| Paginate categories | - | ✔ |
| Delete selected categories | - | ✔ |
| Export categories CSV | - | ✔ |
| Search categories with pagination | - | ✔ |
| Use the buttons below to download. ↓ | BASIC | PRO |
What’s Next?
Next, we will learn how to use this API with a user interface made with JavaScript. Let's learn our JavaScript CRUD tutorial.
What students say?
Don't just take our word for it. See what our students have to say about our tutorials and source codes. We are proud to have helped many individuals and businesses to build their own applications. Here are a few of the testimonials from our satisfied students.
★★★★★ “Wow, I love you guys! The best web programming tutorial I’ve ever seen. So comprehensive, yet easy to follow. I love how you combine all necessary elements in such a neat structure.” ~ Olaug Nessa
★★★★★ “The fact that you’ve put it all together saves so much time and its worth buying the code. Makes me feel good supporting a developer like yourself. Keep up the good work!” ~ Dan Hudson
★★★★★ “Thanks for making these awesome tutorials! I bought your source codes. To be honest, it’s very readable code and helps me understand a lot of things and how it’s done in PHP. Thanks for that again.” ~ Michael Lammens
★★★★★ “Hey Mike, my name is Leonardo from Argentina. I’ve been reading your blog since like 4 months from now, and I really must say: your tutorials are very good, they has helped me in many of my works… Well, thank you very much man. I really admire your work.” ~ Leonardo
★★★★★ “Words can’t express how grateful I am for the work and the articles you post, had some troubles with doing somethings but your articles as per usual hit the hammer right on the head. They are a great way for expanding upon later too!” ~ Jeremy Smith
Got comments?
At codeofaninja.com, we strive to provide our readers with accurate and helpful How To Create A Simple REST API in PHP? Step By Step Guide! Your feedback is essential in helping us achieve this goal.
If you have encountered any issues with the code, have suggestions for improvement, or wish to provide praise, we welcome you to leave a comment below. Please be as descriptive as possible to address your concerns effectively and include any relevant error messages, screenshots, or test URLs.
We request that comments remain on-topic and relevant to the article above. If your question or comment pertains to a different topic, we recommend seeking assistance elsewhere.
Furthermore, we ask that you review our code of conduct before commenting to ensure that your feedback is constructive and respectful.
Thank you for taking the time to provide feedback and for supporting codeofaninja.com. Your contributions help us improve our tutorials and serve the developer community better.
Subscribe for FREE!
Improve your web development skills and stay ahead of the competition by subscribing to our tutorial series. Sign up for FREE and access exclusive, cutting-edge content delivered straight to your inbox.
Take advantage of the chance to elevate your skills and advance your web development career. Subscribe now.
Thank You!
We hope you've found our How To Create A Simple REST API in PHP? Step By Step Guide! helpful and informative. We understand that learning new programming concepts can be challenging, but we're glad we could make it easier for you.
Thank you for choosing to learn with us and for supporting codeofaninja.com! Consider sharing this tutorial with your friends and colleagues who may also be interested in learning about How To Create A Simple REST API in PHP? Step By Step Guide!
The more people know about our tutorials, the more we can help the developer community grow. Keep learning, keep coding, and keep growing as a developer. We can't wait to see what you'll create next!

Hi! I'm Mike Dalisay, the co-founder of codeofaninja.com, a site that helps you build web applications with PHP and JavaScript. Need support? Comment below or contact [email protected]
I'm also passionate about technology and enjoy sharing my experience and learnings online. Connect with me on LinkedIn, Twitter, Facebook, and Instagram.

